Selective removal of Cu2−x(S,Se) phases from Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin films†
Abstract
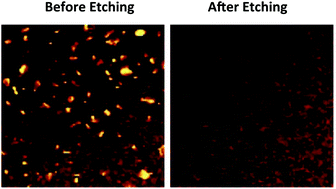
The selective removal of Cu2−x(S,Se) impurity phases from Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) and Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS) thin films is a major barrier to achieving high efficiencies in solar cells based on these films. A toxic and hazardous potassium cyanide (KCN) solution is commonly used as a selective etchant to remove Cu2−x(S,Se) from CZTSSe and CIGS thin films. Herein, we report the selective removal of Cu2−x(S,Se) compounds from kesterite CZTSSe thin films using a mixture of ethylenediamine and 2-mercaptoethanol, a safer chemical mixture than KCN. We found that Cu2−xS and kesterite CZTS nanocrystals dissolve in this mixture in seconds and 6 hours, respectively, while wurtzite CZTS nanocrystals do not dissolve even after 6 hours. Etching CZTSSe thin films containing small amounts of Cu2−x(S,Se) phases for 20 minutes removes the Cu2−x(S,Se) phases completely.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...