Water-in-oil microemulsions versus emulsions as carriers of hydroxytyrosol: an in vitro gastrointestinal lipolysis study using the pHstat technique
Abstract
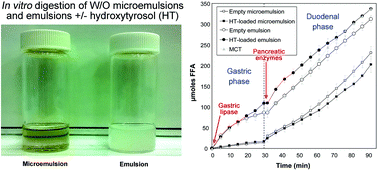
Water-in-oil (W/O) microemulsions and emulsions based on medium chain triglycerides (MCT) were successfully formulated with the addition of emulsifiers and used as encapsulation matrices for hydroxytyrosol (HT), an antioxidant naturally found in extra virgin olive oil. The digestibility of these edible W/O dispersions by recombinant dog gastric lipase (rDGL) and porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) was then tested at different pH values using a pHstat device. rDGL and PPL displayed a much lower activity on the W/O microemulsion than that on the W/O emulsion and MCT alone. This was explained by the presence of higher amounts of emulsifiers (4.9% w/w lecithin and monoglycerides) in the composition of W/O microemulsions compared to W/O emulsions (1.3% w/w emulsifiers). These surfactants also induced a shift of maximum lipase activity towards lower pH values, which usually reflects the competition between surfactants and lipases for binding at the lipid–water interface. rDGL and PPL were then used consecutively in a two-step digestion model mimicking the conditions found in the human gastrointestinal tract. Direct titration and back-titration of free fatty acids allowed the continuous estimation of lipolysis rates under both gastric and duodenal conditions. Gastric lipolysis of W/O microemulsions was reduced 6 to 9-fold compared to W/O emulsions. This inhibition had a major impact on the overall lipolysis, although duodenal lipolysis was less affected by the dispersion type. The presence of HT had also some minor effects on lipolysis rates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...