Inhibition of LPS-induced inflammatory mediators by 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid in macrophages through suppression of PI3K/NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
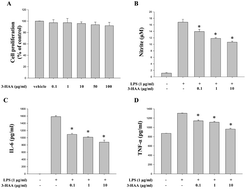
Many tryptophan metabolites have immunomodulatory effects on various immune cells. 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid (3-HAA) is a tryptophan metabolite reported to have anti-inflammatory activity. The mechanism of this activity is unclear. The present study examined the immunomodulatory effects and molecular mechanisms of 3-HAA on macrophages. Pretreatment of 3-HAA (0.1–10 μg mL−1) for 2 h markedly inhibited NO and cytokine production in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells. Moreover, translocation and activation of NF-κB by LPS in the nucleus were abrogated through the prevention of IκB degradation by 3-HAA treatment. 3-HAA significantly suppressed LPS-induced PI3K/Akt/mTOR activation, whereas MAPKs were not affected by 3-HAA treatment. Furthermore, the inhibition of mTOR by 3-HAA resulted in decreased production of inflammatory mediators and NF-κB activity. Similar results were also observed in primary peritoneal macrophages. Furthermore, 3-HAA modulated macrophage polarization. Collectively, the results suggest that 3-HAA has an immunomodulatory effect that may result from inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and NF-κB activation, thereby decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...