Effects of simulated acid rain on soil respiration and its components in a subtropical mixed conifer and broadleaf forest in southern China
Abstract
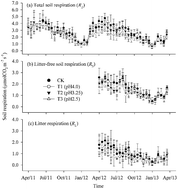
Soil respiration is a major pathway in the global carbon cycle and its response to environmental changes is an increasing concern. Here we explored how total soil respiration (RT) and its components respond to elevated acid rain in a mixed conifer and broadleaf forest, one of the major forest types in southern China. RT was measured twice a month in the first year under four treatment levels of simulated acid rain (SAR: CK, the local lake water, pH 4.7; T1, water pH 4.0; T2, water pH 3.25; and T3, water pH 2.5), and in the second year, RT, litter-free soil respiration (RS), and litter respiration (RL) were measured simultaneously. The results indicated that the mean rate of RT was 2.84 ± 0.20 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1 in the CK plots, and RS and RL contributed 60.7% and 39.3% to RT, respectively. SAR marginally reduced (P = 0.08) RT in the first year, but significantly reduced RT and its two components in the second year (P < 0.05). The negative effects were correlated with the decrease in soil microbial biomass and fine root biomass due to soil acidification under the SAR. The temperature coefficients (Q10) of RT and its two components generally decreased with increasing levels of the SAR, but only the decrease of RT and RL was significant (P < 0.05). In addition, the contribution of RL to RT decreased significantly under the SAR, indicating that RL was more sensitive to the SAR than RS. In the context of elevated acid rain, the decline trend of RT in the forests in southern China appears to be attributable to the decline of soil respiration in the litter layer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...