Di and trinuclear rare-earth metal complexes supported by 3-amido appended indolyl ligands: synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity towards isoprene 1,4-cis polymerization†
Abstract
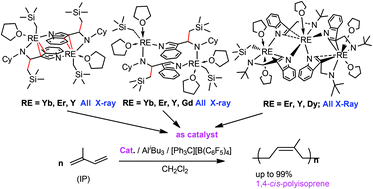
Different di and trinuclear rare-earth metal complexes supported by 3-amido appended indolyl ligands were synthesized and their catalytic activities towards isoprene polymerization were investigated. Treatment of [RE(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 1 equiv. of 3-(CyN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)C8H5NH in toluene or in THF afforded dinuclear rare-earth metal alkyl complexes having indolyl ligands in different hapticities with central metals {[η2:η1–μ–η1-3-(CyNCH(CH2SiMe3))Ind]RE-(thf)(CH2SiMe3)}2 (Cy = cyclohexyl, Ind = Indolyl, RE = Yb (1), Er (2), Y (3)) or {[η1–μ–η1-3-(CyNCH(CH2SiMe3))Ind]RE-(thf)2(CH2SiMe3)}2 (RE = Yb (4), Er (5), Y (6), Gd (7)), respectively. These two series of dinuclear complexes could be transferred to each other easily by only changing the solvents in the process. Reaction of [Er(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 1 equiv. of 3-t-butylaminomethylindole 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF afforded the unexpected trinuclear erbium alkyl complex [η2:η1–μ–η1-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind]4Er3(thf)5(CH2SiMe3) (8), which can also be prepared by reaction of 3 equiv. of [Er(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 4 equiv. of 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF. Accordingly, complexes [η2:η1–μ–η1-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind]4RE3(thf)5(CH2SiMe3) (RE = Y (9), Dy (10)) were prepared by reactions of 3 equiv. of [RE(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 4 equiv. of 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF. Reactions of [RE(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 1 equiv. of 3-t-butylaminomethylindole 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF, followed by treatment with 1 equiv. of [(2,6-iPr2C6H3)N
CH)C8H5NH in toluene or in THF afforded dinuclear rare-earth metal alkyl complexes having indolyl ligands in different hapticities with central metals {[η2:η1–μ–η1-3-(CyNCH(CH2SiMe3))Ind]RE-(thf)(CH2SiMe3)}2 (Cy = cyclohexyl, Ind = Indolyl, RE = Yb (1), Er (2), Y (3)) or {[η1–μ–η1-3-(CyNCH(CH2SiMe3))Ind]RE-(thf)2(CH2SiMe3)}2 (RE = Yb (4), Er (5), Y (6), Gd (7)), respectively. These two series of dinuclear complexes could be transferred to each other easily by only changing the solvents in the process. Reaction of [Er(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 1 equiv. of 3-t-butylaminomethylindole 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF afforded the unexpected trinuclear erbium alkyl complex [η2:η1–μ–η1-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind]4Er3(thf)5(CH2SiMe3) (8), which can also be prepared by reaction of 3 equiv. of [Er(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 4 equiv. of 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF. Accordingly, complexes [η2:η1–μ–η1-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind]4RE3(thf)5(CH2SiMe3) (RE = Y (9), Dy (10)) were prepared by reactions of 3 equiv. of [RE(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 4 equiv. of 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF. Reactions of [RE(CH2SiMe3)3(thf)2] with 1 equiv. of 3-t-butylaminomethylindole 3-(tBuNHCH2)C8H5NH in THF, followed by treatment with 1 equiv. of [(2,6-iPr2C6H3)N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHNH(C6H3iPr2-2,6)] afforded, after workup, the dinuclear rare-earth metal complexes [η1–μ–η1:η1-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind][η1–μ–η1:η3-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind]RE2(thf)[(η3-2,6-iPr2C6H3)NCHN(C6H3iPr2-2,6)]2(RE = Er (11), Y (12)) having the indolyl ligands bonded with the rare-earth metal in different ligations. All new complexes 1–12 were fully characterized by spectroscopic methods and elemental analyses, and their structures were determined by X-ray crystallographic analyses. It was found that, except for complexes 1, 4, 11 and 12, all complexes were highly efficient catalysts for selective isoprene polymerization (up to 99% 1,4-cis selectivity) with the cooperation of co-catalysts, and the trinuclear complexes displayed advantages over dinuclear complexes in terms of molecular weight of polymers.
CHNH(C6H3iPr2-2,6)] afforded, after workup, the dinuclear rare-earth metal complexes [η1–μ–η1:η1-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind][η1–μ–η1:η3-3-(tBuNCH2)Ind]RE2(thf)[(η3-2,6-iPr2C6H3)NCHN(C6H3iPr2-2,6)]2(RE = Er (11), Y (12)) having the indolyl ligands bonded with the rare-earth metal in different ligations. All new complexes 1–12 were fully characterized by spectroscopic methods and elemental analyses, and their structures were determined by X-ray crystallographic analyses. It was found that, except for complexes 1, 4, 11 and 12, all complexes were highly efficient catalysts for selective isoprene polymerization (up to 99% 1,4-cis selectivity) with the cooperation of co-catalysts, and the trinuclear complexes displayed advantages over dinuclear complexes in terms of molecular weight of polymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...