Highly polar solvent-induced disproportionation of a cationic Pt(ii)–diimine complex containing an o-semiquinonato†
Abstract
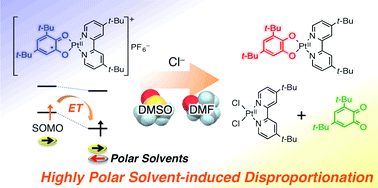
Chemical one-electron oxidation of [PtII(3,5-DTBCat)(DTBbpy)] (1) (3,5-DTBCat = 3,5-di-tert-butyl catecholato, DTBbpy = 4,4′-di-tert-butyl-2,2′-bipyridine) afforded the corresponding paramagnetic complex, [PtII(3,5-DTBSQ)(DTBbpy)]+PF6− (1(PF6)), as a result of ligand-centred oxidation. While complex 1 is relatively stable in common organic solvents, the present study demonstrates that cationic [1]+ is subject to an unprecedented solvent-induced disproportionation in highly polar solvents such as DMSO and DMF, which results in the formation of 1 and a free benzoquinone.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...