Copper complexes as catalyst precursors in the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction†
Abstract
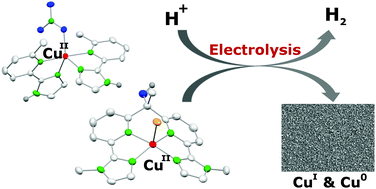
Herein, we report the synthesis and species distribution of copper(II) complexes based on two different ligand scaffolds and the application of the two complexes in the electrochemical proton reduction catalysis. The ligands bind to one or two copper(II) ions and the pH-dependent mono/dinuclear equilibrium depends on the steric bulk of the ligands. The two water soluble copper(II) complexes were investigated for their activities in the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). In both complexes the copper(II) ions have a N4-coordination environment composed of N-heterocycles, although in different coordination geometries (SPY-5 and TBPY-5). The solutions of the complexes were highly active catalysts in water at acidic pH but the complexes decompose under catalytic conditions. They act as precursors for highly active copper(0) and Cu2O deposits at the electrode surface, which are in turn the active catalysts. The absence or presence of the ligands has neither an influence on the catalytic activity of the solutions nor an influence on the activity of the deposit formed during controlled potential electrolysis. Finally, we can draw some conclusions on the stability of copper catalysts in the aqueous electrochemical HER.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...