Photosensitized H2 generation from “one-pot” and “two-pot” assemblies of a zinc-porphyrin/platinum nanoparticle/protein scaffold†
Abstract
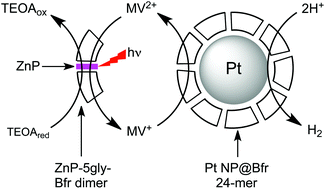
We report photosensitized H2 generation using a protein scaffold that nucleates formation of platinum nanoparticles (Pt NPs) and contains “built-in” photosensitizers. The photosensitizers, zinc-protoporphyrin IX or zinc-mesoporphyrin IX (ZnP) were incorporated in place of the naturally occurring heme in the 24-subunit iron storage protein bacterioferritin (Bfr) when the ZnPs were added to the E. coli expression medium. We engineered a stable dimeric Bfr variant with two protein subunits sandwiching a ZnP. Ten glycines were also substituted in place of residues surrounding the vinyl side of the porphyrin in order increase access of solvent and/or redox agents. An optimized “one-pot” reaction of this glycine-substituted ZnMP-Bfr dimer with a Pt(IV) salt and borohydride resulted in a ∼50 : 50 mixture of protein in the form of Pt-free glycine-substituted ZnP-Bfr dimers and re-assembled 24-mers surrounding Pt NPs formed in situ. H2 production occurred upon visible light irradiation of this “one-pot” product when combined with triethanolamine as sacrificial electron donor and methyl viologen as electron relay. An analogous “two-pot” system containing mixtures of separately prepared Pt-free glycine-substituted ZnP-Bfr dimer and porphyrin-free Pt NP@Bfr 24-mer also showed robust photosensitized H2 generation. The glycine-substituted-ZnP-Bfr dimer thus served as photosensitizer for catalytic reduction of methyl viologen by triethanolamine, and the reduced methyl viologen was able to transfer electrons across the Bfr 24-mer protein shell to generate H2 at the enclosed Pt NP in a “dark” reaction. Our results demonstrate that Bfr is a readily manipulatable and versatile scaffold for photosensitized redox chemistry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...