Investigation of photoelectrical properties of α-Si3N4 nanobelts with surface modifications using first-principles calculations†
Abstract
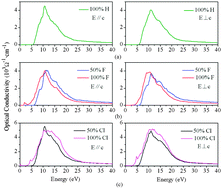
The structural stability, electronic and optical properties of α-Si3N4 nanobelts orientating along the different directions with surface H, F and Cl modifications are investigated using first-principles methods. The stabilities of α-Si3N4 nanobelts are greatly affected by the surface modifications and increased in the order of H, Cl and F. All the modified α-Si3N4 nanobelts exhibit semiconductor characteristics. The effective masses of nanobelts are mainly affected by their orientations as well as surface modifications. The band gaps of α-Si3N4 nanobelts are found to be modulated by surface modifications. The Cl-modified nanobelts result in a smaller band gap than that of H- or F-modified ones. The electronic properties of α-Si3N4 nanobelts have significantly affected their optical properties. The linear light response ranges are mainly located in the ultraviolet region, where the absorption and refraction of light mainly occur, while the reflection is very weak. As the halogen coverage increases to 100%, the absorption edges of α-Si3N4 nanobelts have an obvious red-shift and new dielectric peaks appear. The Cl-modified nanobelts possess higher ε2(ω) peaks, lower absorption edges and better photoelectric characteristics than those of H- or F-modified nanobelts. The static optical parameters ε(0) and n(0) of 100% Cl-modified α-Si3N4 nanobelts are significantly larger than those of other nanobelts, indicating special applications in certain optical components.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...