Swelling of ionic microgel particles in the presence of excluded-volume interactions: a density functional approach
Abstract
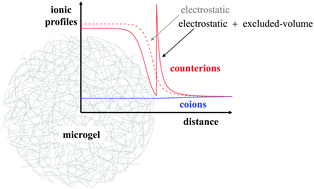
In this work a new density functional theory framework is developed to predict the salt-concentration dependent swelling state of charged microgels and the local concentration of monovalent ions inside and outside the microgel. For this purpose, elastic, solvent-induced and electrostatic contributions to the microgel free energy are considered together with the free energy of the ions. In addition to the electrostatic interaction, the model explicitly considers both the microgel–ion excluded-volume (steric) repulsion and the ionic correlations, in such a way that the formalism is consistent with the Hypernetted-Chain Closure approximation (HNC). We explore the role that the solvent quality, chain elasticity, salt concentration and microgel bare charge play on the swelling state, the effective charge and on the ionic density profiles. Our results show that the microgel–ion steric exclusion foments the increase of the particle size up to 10%. The role that the steric effect plays on the counterion distribution becomes more important when the microgel approaches the shrunken configuration, developing an accumulation peak at the microgel interface and a reduction in the inner core of the microgel that induce a significant increase of the microgel effective charge. We further find that deep inside the particle charge electroneutrality is achieved and a Donnan potential corrected by the steric exclusion is established.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...