Dynamic and static behavior of the H⋯π and E⋯π interactions in EH2 adducts of benzene π-system (E = O, S, Se and Te), elucidated by QTAIM dual functional analysis†
Abstract
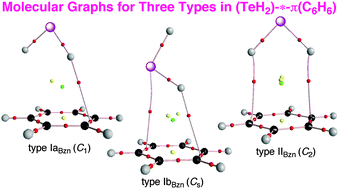
Dynamic and static behavior of the interactions in the EH2 adducts of a benzene π-system (E = O, S, Se and Te) is elucidated by applying QTAIM-DFA (QTAIM dual functional analysis). Two types of H-*-π and E-*-π interactions are detected in the adducts, where the asterisk (*) emphasizes the existence of the bond critical point (BCP) on the interaction in question. Total electron energy densities Hb(rc) are plotted versus Hb(rc) − Vb(rc)/2 [=(ℏ2/8m)∇2ρb(rc)] at BCPs in QTAIM-DFA, where Vb(rc) are the potential energy densities at BCPs. Data from the fully optimized structures are analyzed by polar (R, θ) coordinate representation. Each plot for an interaction, containing data from the perturbed structures with those of the fully optimized one, shows a specific curve, which provides important information. The plot is expressed by (θp, κp): θp corresponds to the tangent line for the plot and κp is the curvature. θ and θp are measured from the y-axis and y-direction, respectively. Moreover, (R, θ) corresponds to the static nature, (θp, κp) represents the dynamic nature of interactions. While θ classifies the interaction in question, θp characterizes it. Both values are less than 90° for all H-*-π and E-*-π interactions examined in this study; therefore, they are all classified by the pure closed-shell interactions and predicted to have the character of vdW nature. However, it is suggested that E-*-π has the nature of the stronger interaction than the case of H-*-π for dynamic behavior in the same species evaluated at the MP2 and M06-2X levels. The nature of the interactions is well analyzed and specified by applying QTAIM-DFA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...