The factors affecting the assembly of Keggin–metal–bimb systems: charge/polarity of Keggin polyanions and coordination modes of metal cations†
Abstract
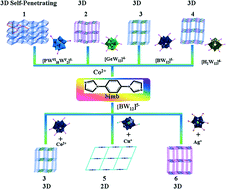
To explore the influence of the charge/polarity of Keggin polyanions and coordination modes of transition metal cations on the construction of polyoxometalate (POM)-based hybrid compounds, we design two synthetic routes and obtain six new POM-based inorganic–organic hybrid compounds, namely, [Co5(H2O)6(bimb)8(PWVI10WV2O40)2]·14H2O (1), [Co2(bimb)2(GeW12O40)][bimb]·2H2O (2), [Co2(bimb)2(BW12O40)][Hbimb]·2H2O (3), [Co2(bimb)2(H2W12O40)][H2bimb]·2H2O (4), [Cu(bimb)(BW12O40)][H2bimb]2·2H2O (5) and [Ag2(bimb)2(BW12O40)][H3bimb]·2H2O (6) (bimb = 1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene). All compounds were characterized by elemental analyses, IR spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Compound 1 represents the first POM-based three-dimensional (3D) self-penetrating structure composed of a unique metal–organic polycatenated framework and tridentate Keggin clusters. Compounds 2, 3, 4 and 6 are isostructural, which show POMOF structures consisting of Keggin cluster guests and a metal–organic nanotube host. The structure of compound 5 is a simple 2D grid layer. The isolation of the title compounds is very informative for systematically understanding the effect of the charge/polarity of POMs and coordination modes of transition metal cations on the structures of POM-based hybrids. The effect of the charge/polarity of POMs and coordination modes of transition metal cations is discussed in this work. Additionally, the luminescence and electrochemical properties of 1–6 have been investigated in detail.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...