Destructive interactions of dirhodium(ii) tetraacetate with β metallothionein rh1a†
Abstract
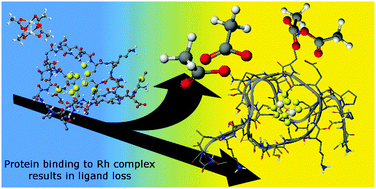
Metal-based therapeutics are vital tools in medicine. Metal-chelating proteins can dramatically decrease drug efficacy. Dirhodium(II) tetraacetate, a potential anticancer compound, binds in vitro to 8 cysteines of the human metallothionein 1a β-fragment. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry shows that the final product is the Rh24+ core encapsulated by the β fragment of the metallothionein protein protein.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...