Determination of copper in composite biomaterials by capillary electrophoresis: an UV-direct method based on in situ complex formation
Abstract
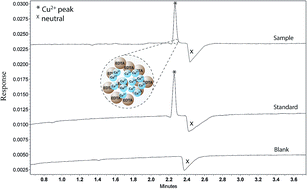
This work describes the optimization and validation of an UV-direct capillary electrophoresis method for the analysis of copper ions in samples obtained from release studies of bone-tissue-engineering composite biomaterials. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid was used as a complexing agent added to the background electrolyte to modulate the selectivity of the separation and quantitation of free copper ions. The separations were performed under reverse polarity and the parameters of validation such as specificity, linearity, limits of detection and quantitation, precision, accuracy and robustness were evaluated. The method resulted to be suitable for copper determination in biomaterials and showed advantages such as rapidness, specificity and suitable sensibility, achieving a limit of detection and quantitation of 0.05 and 0.16 μg mL−1, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...