Fluorescence anisotropy assay for d-vasopressin with a tetramethylrhodamine-labeled aptamer†
Abstract
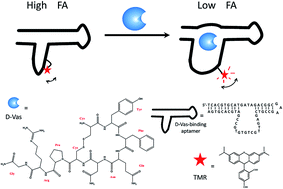
Here we report a fluorescence anisotropy (FA) assay for D-vasopressin (D-Vas), an important active peptide, by using a tetramethylrhodamine (TMR) labeled 55-nt aptamer that contains 19 guanine (G) bases. This assay is based on a target-binding induced change of the intramolecular interaction between TMR and G base and the subsequent FA alteration of labeled TMR. We conjugated single TMR on different labeling positions of thymine (T) bases or terminals of the aptamer, obtaining 14 TMR-labeled aptamers. We screened the FA response of each TMR-labeled aptamer upon D-Vas addition. An aptamer probe with TMR labeled on the 34th base T in sequence exhibited sensitive and significant FA-decreasing responses upon the binding of D-Vas. Under optimized assay conditions this favorable TMR-labeled aptamer allowed direct FA detection of D-Vas ranging from 0.2 μM to 200 μM with good selectivity. This FA method also enabled the detection of D-Vas spiked in diluted serum and urine samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...