Using the L/O ratio to determine blend composition in biodiesel by EASI-MS corroborated by GC-FID and GC-MS†
Abstract
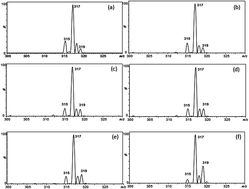
Easy ambient sonic-spray ionization mass spectrometry (EASI-MS) is applied to the analysis of biodiesel blends prepared from soybean and animal fat biodiesel. A correlation was established between the ratio of abundance of linoleic acid (L) and oleic acid (O) methyl ester ions with the biodiesel blend composition. To compare these results from the EASI-MS technique, the L/O ratio of these blends was also determined using both gas chromatography with flame ionization detection (GC-FID) and gas chromatography with mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Both these classical techniques confirmed that the ratio between the mass fraction of FAME from L and O as measured by EASI-MS is indeed correlated with the blend composition of soybean–animal fat biodiesel.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...