Prevention of surface-induced thrombogenesis on poly(vinyl chloride)†
Abstract
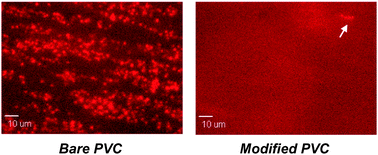
Much biomedical equipment consisting of or containing plastic polymer(s) must come into contact with blood – an interaction that, at the molecular level, may unfortunately prompt biological processes with potentially deleterious, short- or long-term effects such as thrombosis. In the present investigation, this problem is alleviated for poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) through chemical surface modification with an ultrathin, monoethylene glycol-based coating – a transformation that is characterized using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) supplemented by contact angle goniometry (CAG). Antithrombogenic properties are assessed through calculation (for the first 10 min, and after 60 min) of the surface coverage percentage due to platelet adhesion, aggregation and thrombus formation upon continuous exposure to fluorescently-labelled whole human blood. At all shear rates investigated (300, 900, and 1500 s−1), surface coverage decreases by >99% with respect to bare PVC (10 min, short-term contact with blood). Most importantly, antithrombogenic performance is retained for longer-term exposure experiments (60 min), regardless of applied shear rate as well.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...