Designing compartmentalized hydrogel microparticles for cell encapsulation and scalable 3D cell culture†
Abstract
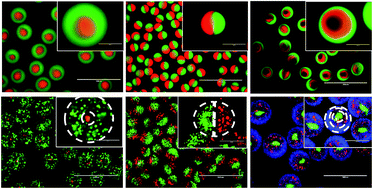
We describe here designs of compartmentalized hydrogel microparticles with a tunable extracellular matrix (ECM) support for cell encapsulation and scalable 3D cell culture. The microparticles, rapidly formed by a one-step, multi-fluidic electrostatic spraying technique (>10 000 min−1), have a uniform spherical shape, a nearly monodisperse size distribution and controlled compartmentalization. They not only have a high surface area for mass transfer but also offer defined space and essential ECM support for various scalable and efficient 3D cell culture, co-culture and microtissue production applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...