Co@NH2-MIL-125(Ti): cobaloxime-derived metal–organic framework-based composite for light-driven H2 production†
Abstract
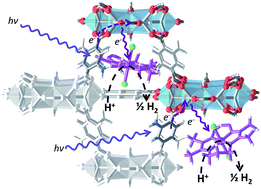
We present a synthetic strategy for the efficient encapsulation of a derivative of a well-defined cobaloxime proton reduction catalyst within a photoresponsive metal–organic framework (NH2-MIL-125(Ti)). The resulting hybrid system Co@MOF is demonstrated to be a robust heterogeneous composite material. Furthermore, Co@MOF is an efficient and fully recyclable noble metal-free catalyst system for light-driven hydrogen evolution from water under visible light illumination.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...