The HAlF4 superacid fragmentation induced by an excess electron attachment
Abstract
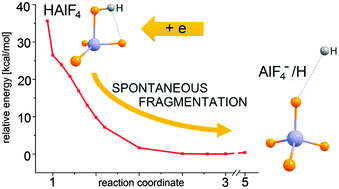
The excess electron attachment to the HAlF4 superacid molecule was studied by employing ab initio CCSD(T) and MP2 methods and a purposely suited aug-cc-pVTZ+4s4p3d basis set. The results indicate that the HAlF4 molecule, due to its polarity, may attract a distant excess electron and form a dipole-bound anionic state whose vertical electron binding energy is 1106 cm−1. The initially formed (HAlF4)− anion of a dipole-bound nature undergoes an immediate structural reorganization driven by the (AlF4)− strongly-bound superhalogen anion formation. The potential energy surface analysis leads to the conclusion that the (HAlF4)− → (AlF4)− + H transformation should proceed spontaneously and involve the simultaneous structure relaxation of the AlF4 moiety (in the direction approaching a tetrahedral geometry) and the excess electron density migration from the area outside the molecular framework to the valence AlF4 region. The fragmentation of the HAlF4 superacid molecule is predicted to be the final effect of the excess electron attachment process. In addition, the important antenna role of the initially formed (HAlF4)− dipole-bound anionic state is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...