Radiative and non-radiative decay rate of K2SiF6:Mn4+ phosphors
Abstract
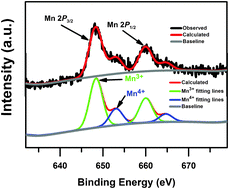
Mn4+-activated K2SiF6 phosphors for use in light emitting diode (LED) applications have recently attracted a great deal of attention since they exhibit an advantage over conventional wide band-type red-light-emitting phosphors. K2SiF6:Mn4+ phosphors have shown extremely narrow emission peaks in wavelengths ranging from 620 to 630 nm, leading to a higher color-rendering index and larger color gamut for the final LED applications. We examined the decay behavior in terms of radiative and non-radiative rates along with a reliable evaluation of Mn4+ concentrations. Inter-activator energy transfer played a significant role in the luminescence process in this well-known narrow peak emission type of the red phosphor K2SiF6:Mn4+.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...