Formulation of robust organic–inorganic hybrid magnetic microcapsules through hard-template mediated method for efficient enzyme immobilization
Abstract
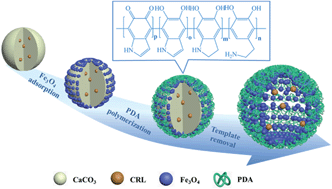
A mild and facile method for the construction of robust organic–inorganic hybrid magnetic microcapsules was developed by a hard-template mediated method combined with polydopamine (PDA) and Fe3O4 nanoparticles onto a CaCO3 microparticle template. More specifically, negatively charged Fe3O4 nanoparticles were adsorbed on the surface or into the lumen of porous CaCO3 microparticles through electrostatic interaction and physical absorption. Then, the magnetic sacrificial templates were coated with PDA through the self-polymerization of dopamine to obtain the magnetic PDA–CaCO3 microparticles, which was followed by template removal using EDTA to construct organic–inorganic hybrid magnetic microcapsules. Characterization confirmed that the microcapsules possess a robust hollow structure such that the enzyme inside exists in a free state. The Fe3O4 nanoparticles acted as critical factors in the microcapsules for both recyclable component and tough scaffolds to sustain the microcapsules away from collapsing and folding. Combing the merits of the organic layer and the inorganic component, the microcapsules were applied for the encapsulation of Candida Rugosa Lipase (CRL). The encapsulated CRL was demonstrated to have several advantages, including increased encapsulation efficiency, enzyme activity and long-term storage stability. Hopefully, the as-prepared microbioreactor may provide a facile and generic approach for other biochemical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...