LiFePO4/NaFe3V9O19/porous glass nanocomposite cathodes for Li+/Na+ mixed-ion batteries†
Abstract
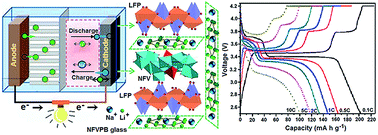
The discovery and optimisation of high performance cathode materials are critical to future breakthroughs for next-generation rechargeable batteries. LiFePO4 (LFP)/NaFe3V9O19 (NFV)/Na2O–FeO–V2O3–P2O5–biocarbon (NFVPB) porous glass nanocomposites (LFP/NFV/NFVPB) offer new possibilities for Li+/Na+ mixed-ion batteries with high-rate capability and high discharge voltage plateaus. Here we have successfully synthesized these nanocomposites via self-assembly of adenosine disodium triphosphate (Na2ATP) biotemplates and a carbon thermal reduction method. As a novel cathode material, LFP/NFV/NFVPB delivers a reversible capacity of 202.8 mA h g−1 at 0.1C in the Li+/Na+ mixed-ion cell with the electrochemically active redox reactions of Fe2+/Fe3+ and V3+/V4+, which is far higher than the theoretical capacity of LiFePO4 (170 mA h g−1). The cell exhibits two high voltage plateaus with well-defined discharge voltage near 3.4 and 3.7 volts, and a coulombic efficiency of approximately 90 percent. Because the low-energy nonequilibrium paths of the fast phase transformation process in LFP/NFV composite nanoparticles can improve the high-rate performance, the cell still exhibits a higher specific capacity of about 100.4 mA h g−1 at 10C. These results are attributed to the nanocomposite structure of LiFePO4 and NaFe3V9O19 and better percolation of electrochemically active glass with a hierarchical pore structure. This work will contribute to the development of Li+/Na+ mixed-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...