Mercaptophosphonic acids as efficient linkers in quantum dot sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
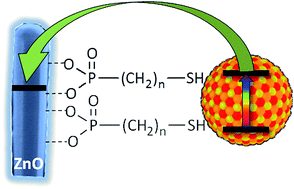
Control over the deposition of quantum dots (QDs) on nanostructured semiconductors is very important for the photovoltaic performance of QD sensitized solar cells. The best control is typically achieved using bifunctional molecular linkers, such as mercaptopropionic acid (MPA), to attach the QDs to metal oxides in a specific manner; however some materials, such as ZnO, are not compatible with these molecules due to their pH sensitivity. We have developed new linkers, mercaptophosphonic acids of different length, which allow efficient functionalization of ZnO nanowires and also mesoporous TiO2 without damaging their surface. Detailed XPS and contact angle studies of the mechanism of self-assembly of these acids show that their strong chelation of the oxide surface prevents protonic attack and etching. Using these linkers, we show that colloidal ternary quantum dots, CuInS2, can be conformally and homogeneously deposited on the functionalized metal oxides. Photophysical studies by means of time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy confirm efficient electron transfer from the QDs to the metal oxides with the rate and efficiency scaling with respect to the linker length and nature. The efficiency of the QD sensitized solar cells fabricated with such assemblies also strongly depends on the linkers used and follows the trends observed for the charge transfer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...