Improvement of the power conversion efficiency and long term stability of polymer solar cells by incorporation of amphiphilic Nafion doped PEDOT-PSS as a hole extraction layer†
Abstract
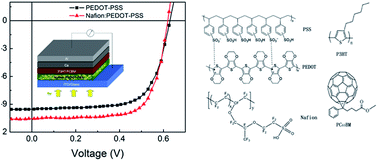
PEDOT-PSS is a widely used hole extraction layer in polymer solar cells (PSCs). However, its acidic and hygroscopic nature usually affects the long-term stability of photovoltaic devices. Herein, we report an effective method to enhance the conductivity and stability of the PEDOT-PSS film by doping with an amphiphilic perfluorosulfonic copolymer, Nafion. The highly hydrophobic fluorocarbon backbone of Nafion preferentially interacts with the hydrophobic PEDOT of PEDOT-PSS, while the highly hydrophilic –SO3H groups preferentially interact with hydrophilic PSS chains, inducing the PEDOT chains to separate from the PSS chains by Nafion. The conductivity and surface morphology of the Nafion-doped PEDOT-PSS layer were investigated by using a four-point probe and an atomic force microscope, respectively. The optical properties of the Nafion doped PEDOT-PSS film and the photoactive layer spin-coated on it were studied by transmittance and reflection spectra. With the Nafion doped PEDOT-PSS hole extraction layer (HEL), the power conversion efficiency of the PSCs based on poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) and [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) reaches 4.63%, increased by 14.3% in comparison with that of the control devices. Furthermore, the lifetime of the devices with Nafion doped PEDOT-PSS HEL is greatly enhanced.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...