Aluminum borohydride–ethylenediamine as a hydrogen storage candidate†
Abstract
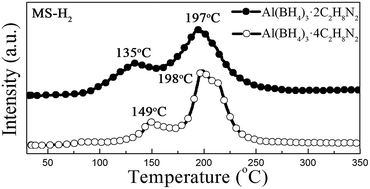
A series of novel hydrogen storage compounds (Al(BH4)3·nC2H8N2, n = 4, 3, 2, 1) were synthesized. This system turned out to be a reliable hydrogen storage candidate and a maximum of 10.4 wt% pure hydrogen was achieved below 350 °C. Further investigation revealed that the coordination number has a significant impact on their dehydrogenation properties, enabling tunable dehydrogenation of the system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...