Electrochemical detection of azidothymidine on modified probes based on chitosan stabilised silver nanoparticles hybrid material†
Abstract
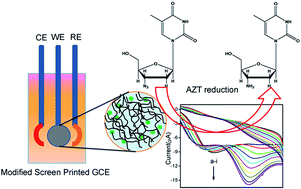
The present work deals with the development of chitosan (Ch) stabilized silver nanoparticles (Ch@Ag NPs) hybrid material modified screen printed graphite electrodes (SPGE) for electrochemical detection of azidothymidine (AZT). AZT is an antiretroviral (ARV) drug used for the treatment of persons infected with HIV-1. Ch@Ag NPs have been synthesized successfully using one pot chemical synthesis approach. As-synthesized Ch@Ag NPs are characterized by various techniques like UV-vis, zeta potential, FT-IR, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and cyclic voltammetry techniques. This hybrid material is used for the development of sensing probes. Before development of SPGE based sensing probes, first we modified commercial glassy carbon electrode (GCE) by Ch@Ag NPs (Ch@Ag NPs/GCE) in order to check the capability of this hybrid nanomaterial towards electroactivity and detection of AZT. The catalytic effect of this hybrid is explained based on coordination ability with AZT molecules and excellent electroactivity due to the large energetic surface of Ag NPs. Thereafter, modification is extended using Ch@Ag NPs on SPGE (Ch@Ag NPs/SPGE) for developing cost effective portable sensors. As-modified Ch@Ag NPs/GCE has been used for AZT detection in the wide range of concentration from 1.0 μM to 718 μM in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH = 7.6) using voltammetric techniques. Further AZT is also successfully detected over Ch@Ag NPs/SPGE in the concentration range of 10 μM to 533 μM in phosphate buffer solution as well as in biological samples (human plasma) using simple cyclic voltammetric technique. The limit of detection (LOD) of Ch@Ag NPs/SPGE is found to be 1 μM in PBS and 10 μM in biological samples (human plasma) at S/N (signal to noise ratio): 3.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...