First investigation of polyoxoniobate and polyoxotantalate aqueous speciation by capillary zone electrophoresis†
Abstract
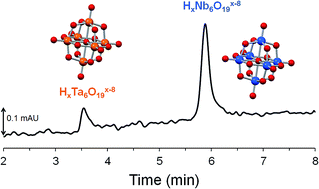
Aqueous solutions of hexaniobate (HxNb6O19x−8, 0 ≤ x ≤ 3) and hexatantalate ions (HxTa6O19x−8, 0 ≤ x ≤ 3) have been probed by capillary zone electrophoresis (CE) for the first time. Taking advantage of the UV properties of HxTa6O19x−8 and HxNb6O19x−8, the detection of Nb(V) and Ta(V) could be performed without using toxic or expensive chelating reagents as reported in CE methods previously developed for Nb and Ta samples. The effective electrophoretic mobilities of the hexaniobate and hexatantalate ions were measured as a function of pH in Li+, Na+ and K+-based alkaline media at 25 °C. Although HxTa6O19x−8 and HxNb6O19x−8 have almost identical electronic and structural features, they were easily separated in a wide pH range (9 to 13) using standard bare-fused silica capillary. The separation of Nb and Ta was accomplished in 5 minutes, which affords a promising method for the analytical support of industrial processes. The striking difference observed in the mobilities of HxTa6O19x−8 and HxNb6O19x−8 also led to new insights regarding the ion-association behavior of these highly charged species.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...