Gas barrier properties of polymer/clay nanocomposites
Abstract
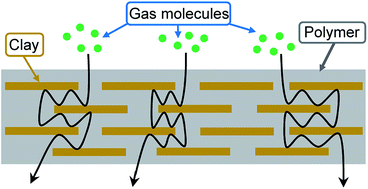
In the field of nanotechnology, polymer nanocomposites (PNCs) have attracted both academic and industrial interest due to their exceptional electrical, mechanical and permeability properties. In this review, we summarize the state-of-the-art progress on the use of platelet-shaped fillers for the gas barrier properties of PNCs. Layered silicate nanoclays (such as montmorillonite and kaolinite) appear to be the most promising nanoscale fillers. These exfoliated nanofillers are able to form individual platelets when dispersed in a polymer matrix. The nanoplatelets do not allow diffusion of small gases through them and are able to produce a tortuous path which works as a barrier structure for gases. The utilization of clays in the fabrication of PNCs with different polymer matrices is explored. Most synthesis methods of clay-based PNCs are covered, including, solution blending, melt intercalation, in situ polymerization and latex compounding. The structure, preparation and gas barrier properties of PNCs are discussed in general along with detailed examples drawn from the scientific literature. Furthermore, details of mathematical modeling approaches/methods of gas barrier properties of PNCs are also presented and discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...