Preparation and characterization of chitosan/silver nanoparticle/copper nanoparticle/carbon nanotube multifunctional nano-composite for water treatment: heavy metals removal; kinetics, isotherms and competitive studies†
Abstract
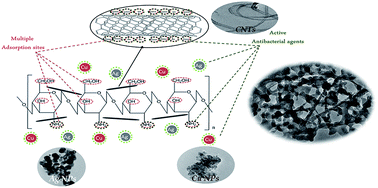
In this work, a multifunctional nanocomposite of chitosan, silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs), copper nanoparticles (Cu NPs) and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) has been successfully prepared. The structure has been confirmed using X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmittance electron microscopes. CNTs, Ag NPs and Cu NPs are distributed homogeneously inside the polymer matrix. The adsorption efficiency of chitosan for Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) reached 60% using 5 g L−1 adsorbent dose while for the multifunctional composite, it reached 100% adsorption efficiency with a reduction of the amount of adsorbent to 1 g L−1. For the multifunctional composite, 10 min is enough for almost complete removal of metal ions from the solution while for chitosan the efficiency is rather lower. The adsorption process fitted to the pseudo-second order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm in the linear form in case of chitosan while in case of the multifunctional composite, it fitted to the pseudo-second order kinetic model and Langmuir and Freundlich models in the non-linear forms. The maximum amount adsorbed (Qmax) was found to be directly related to and fitted well with the electrode potential values of metal ions in case of chitosan while for the multifunctional composite, the ionic radius is the most dependent parameter. The multifunctional composite was found to be regenerated effectively using EDTA solution for up to five efficient cycles of adsorption/desorption processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...