Electrochemical detection of a pathogenic Escherichia coli specific DNA sequence based on a graphene oxide–chitosan composite decorated with nickel ferrite nanoparticles†
Abstract
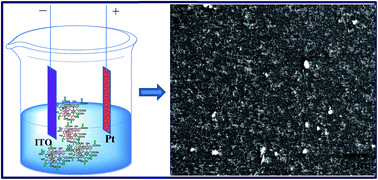
In this report, an electrochemical genosensor has been fabricated for Escherichia coli O157:H7 (E. coli) detection using a graphene oxide–nickel ferrite–chitosan (GO/NiF/ch) nanocomposite film as the sensing platform. The prepared GO/NiF/ch nanocomposite was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermo-gravimetric analysis. Nucleic acid hybridization technique was employed for the detection of a specific sequence of E. coli. The hybridization between the complementary DNA and probe DNA was investigated by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) using methylene blue as redox indicator. The fabricated biosensor exhibits a linear response to complementary DNA in the concentration range of 10−6 to 10−16 M with a detection limit of 1 × 10−16 M.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...