Preparation and characterization of a novel porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT/PbO2 electrode for the anodic oxidation of phenol wastewater
Abstract
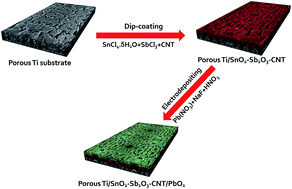
Porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT/PbO2 electrodes were successfully fabricated using a thermal decomposition technique and electro-deposition technologies. Characterization experiments including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and an accelerated lifetime test were performed to evaluate the effect of the CNT-doped SnO2–Sb2O3 intermediate layer on the PbO2 electrode. The results showed that CNT could be doped into the SnO2–Sb2O3 intermediate layer by thermal decomposition. Compared with the porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3 substrate, CNT-doping induced the substrate surface to form a fibrous structure, which suggested that the porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT substrate would provide more active sites for PbO2 deposition and could make a compact and fine surface coating. Moreover, the CNT-modified electrode had a higher active surface area and higher electrochemical activity than that without CNT doping. The life of the porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT/PbO2 electrode (296 h) was 1.38 times as much as that of the porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 electrode (214 h). The electro-catalytic oxidation of phenol in an aqueous solution was studied to evaluate the electrochemical oxidation ability in environmental applications. The porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT/PbO2 electrode displayed not only excellent electro-catalytic performance but also a low energy consumption using phenol as a model organic pollutant. The porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT/PbO2 electrode has a higher kinetic rate constant and chemical oxygen demand (COD), which is 1.73 and 1.09 times those of the porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 electrode, respectively. Moreover, CNT-doping can further increase the hydroxyl radical (˙OH) generation capacity. All these results illustrated that the porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3–CNT/PbO2 electrode could be used for pollutant degradation and had a great application potential.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...