Electrochemical determination of phenanthrene based on anthraquinone sulfonate and poly diallyldimethylammonium chloride modified indium–tin oxide electrode
Abstract
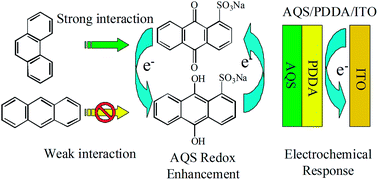
In this paper, specific electrochemical interaction between phenanthrene (Phe) and anthraquinone sulfonate (AQS) was first investigated by Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) and Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV). Poly diallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA) and AQS were modified onto indium–tin oxide (AQS/PDDA/ITO) by self-assembling. Owing to the specific interaction between AQS and Phe, the amount of Phe could be quantified by the electrochemical oxidation peak current difference of AQS at AQS/PDDA/ITO in the range from 1.0 × 10−12 to 1.0 × 10−9 mol L−1 with a linearity (r = 0.9942) and a low detection limit of 5.0 × 10−13 mol L−1 (S/N = 3). As an example of its practical application, the new sensor was used for quantitative determination of Phe in a standard sample and cloud-rain water samples of Mount Taishan with satisfactory results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...