Surface modification of polyamide composite membranes by corona air plasma for gas separation applications
Abstract
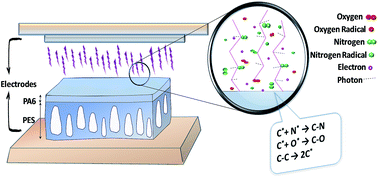
In this study, dual-layer polyamide 6/polyethersulfone (PA6/PES) composite membranes were prepared via the phase inversion technique and corona air plasma was employed to modify the membrane surface in order to improve the gas separation performance. The effect of corona treatment parameters like exposure time and input power on the membrane surface properties, morphology and separation performance was investigated. The gas separation performance of the membranes before and after the corona treatment was evaluated by permeation measurements for CO2, O2 and N2 gases. The FTIR-ATR, SEM, AFM and contact angle analyses were used to characterize the untreated and corona treated membranes. The FTIR-ATR and contact angle results indicated that the corona treatment introduced polar groups on the membrane surface and led to significant enhancement in the membrane polarity, hydrophilicity and wettability. The gas permeation results revealed that the permeability and selectivity of the modified membranes were changed dramatically due to surface ablation and formation of polar groups depending on the corona treatment conditions. An increase in corona treatment time and input power resulted in higher gas permeability, however corona modification at high power and longer exposure time led to a membrane with low gas selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...