Sulfamethazine copper(ii) complexes as antimicrobial thermal stabilizers and co-stabilizers for rigid PVC: spectroscopic, thermal, and DFT studies†
Abstract
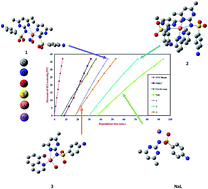
[CuL2(OH2)]·1.5H2O (1), [CuL2(bpy)]·0.66H2O (2) and [CuLQ(OH2)]·H2O (3) (HL = sulfamethazine, bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine and HQ = 8-hydroxyquinoline) complexes were prepared, characterized (elemental analysis, infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, magnetic and conductivity measurement), and tested for their antibacterial activity. Coordination of HL to the Cu(II) ion did not markedly change its toxicity, but the presence of a secondary ligand gave rise to lower activity. Sulfamethazine and its complexes have been investigated as thermal stabilizers and co-stabilizers for rigid poly(vinyl chloride). A synergism has been achieved when the investigated compounds were mixed in an equivalent weight ratio with the reference stabilizers. The experimental studies have been complemented by density functional theory data in terms of optimization, natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis, and molecular electrostatic potential maps. The structural-thermal stabilization relationship showed that energy of the highest occupied molecular orbital, ΔE, and softness were the most useful descriptors for the correlation with the thermal stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...