Long-term release of a thiobenzamide from a backbone functionalized poly(lactic acid)†
Abstract
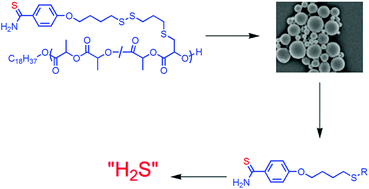
Hydrogen sulfide is emerging as a critically important molecule in medicine, yet there are few methods for the long-term delivery of molecules that degrade to release H2S. In this paper the first long-term release of a thiobenzamide that degrades to release H2S is described. A series of polymers were synthesized by the copolymerization of L-lactide and a lactide functionalized with 4-hydroxythiobenzamide. A new method to attach functional groups to a derivative of L-lactide is described based on the addition of a thiol to an α,β-unsaturated lactide using catalytic I2. This reaction proceeded under mild conditions and did not ring-open the lactone. The copolymers had molecular weights from 8 to 88 kg mol−1 with PDIs below 1.50. Two sets of microparticles were fabricated from a copolymer; the average diameters of the microparticles were 0.53 and 12 μm. The degradation of the smaller microparticles was investigated in buffered water to demonstrate the slow release of thiobenzamide over 4 weeks. Based on the ability to synthesize polymers with different loadings of thiobenzamide and that thiobenzamide is a known precursor to H2S, these particles provide a polymer-based method to deliver H2S over days to weeks.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...