Synthesis of chitin and chitosan stereoisomers by thermostable α-glucan phosphorylase-catalyzed enzymatic polymerization of α-d-glucosamine 1-phosphate†
Abstract
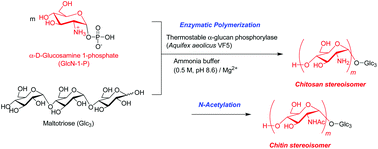
The relationship between two aminopolysaccharide stereoisomers, namely α-(1→4)- and β-(1→4)-linked (N-acetyl)-D-glucosamine polymers, is of significant interest within the field of polysaccharide science, as they correspond to amino analogs of the representative abundant natural polysaccharides, viz. amylose and cellulose. While the latter glucosamine polymer is the basis of well-known natural polysaccharides, chitin and chitosan (linear polysaccharides composed of β-(1→4)-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine), to the best of our knowledge, the former (α-(1→4)-linked) has not been observed in nature. For the purpose of these studies, the synthesis of such non-natural aminopolysaccharides was performed by the thermostable α-glucan phosphorylase (from Aquifex aeolicus VF5)-catalyzed enzymatic polymerization of α-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate (GlcN-1-P), via successive α-glucosaminylations, in ammonia buffer containing Mg2+ ions, resulting in the production of the α-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine polymers, corresponding to the structure of the chitosan stereoisomer. Subsequent N-acetylation of the products gave the aminopolysaccharides, corresponding to the chitin stereoisomer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...