Chondroitin sulfate-polyethylenimine copolymer-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as an efficient magneto-gene carrier for microRNA-encoding plasmid DNA delivery†
Abstract
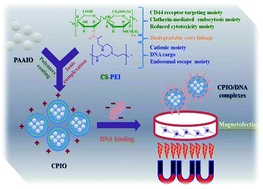
MicroRNA-128 (miR-128) is an attractive therapeutic molecule with powerful glioblastoma regulation properties. However, miR-128 lacks biological stability and leads to poor delivery efficacy in clinical applications. In our previous study, we demonstrated two effective transgene carriers, including polyethylenimine (PEI)-decorated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) as well as chemically-conjugated chondroitin sulfate-PEI copolymers (CPs). In this contribution, we report optimized conditions for coating CPs onto the surfaces of SPIONs, forming CPIOs, for magneto-gene delivery systems. The optimized weight ratio of the CPs and SPIONs is 2 : 1, which resulted in the formation of a stable particle as a good transgene carrier. The hydrodynamic diameter of the CPIOs is ∼136 nm. The gel electrophoresis results demonstrate that the weight ratio of CPIO/DNA required to completely encapsulate pDNA is ≥3. The in vitro tests of CPIO/DNA were done in 293 T, CRL5802, and U87-MG cells in the presence and absence of an external magnetic field. The magnetofection efficiency of CPIO/DNA was measured in the three cell lines with or without fetal bovine serum (FBS). CPIO/DNA exhibited remarkably improved gene expression in the presence of the magnetic field and 10% FBS as compared with a gold non-viral standard, PEI/DNA, and a commercial magnetofection reagent, PolyMag/DNA. In addition, CPIO/DNA showed less cytotoxicity than PEI/DNA and PolyMag/DNA against the three cell lines. The transfection efficiency of the magnetoplex improved significantly with an assisted magnetic field. In miR-128 delivery, a microRNA plate array and fluorescence in situ hybridization were used to demonstrate that CPIO/pMIRNA-128 indeed expresses more miR-128 with the assisted magnetic field than without. In a biodistribution test, CPIO/Cy5-DNA showed higher accumulation at the tumor site where an external magnet is placed nearby.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...