Synthesis of NiCo2O4/Nano-ZSM-5 nanocomposite material with enhanced electrochemical properties for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and tryptophan†
Abstract
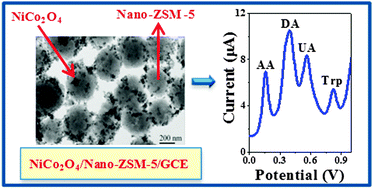
NiCo2O4/Nano-ZSM-5 nanocomposite materials were prepared by the calcination of a physical mixture of NiCo2O4 and Nano-ZSM-5. The materials were characterized by the complementary combination of X-ray diffraction, N2-adsorption and electron microscopic techniques. An electrochemical sensor based on NiCo2O4/Nano-ZSM-5 nanocomposite was constructed for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, and tryptophan. Among the materials investigated in this study, the NiCo2O4 (30%)/Nano-ZSM-5 modified glassy carbon electrode exhibited the highest electrocatalytic activity with excellent stability, sensitivity, and selectivity. Under the optimum conditions, wide linear ranges were obtained from 1–1200 μM for ascorbic acid, 0.6–900 μM for dopamine, 0.9–1000 μM for uric acid, and 0.9–1000 μM for tryptophan. The detection limits were found to be 0.8, 0.5, 0.7 and 0.7 μM for ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, and tryptophan, respectively. The analytical performance of the developed sensor was demonstrated in the determination of ascorbic acid and dopamine in commercial pharmaceutical preparations (vitamin C tablets and dopamine injections) and uric acid in human urine samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...