Sulfasalazine in ionic liquid form with improved solubility and exposure†
Abstract
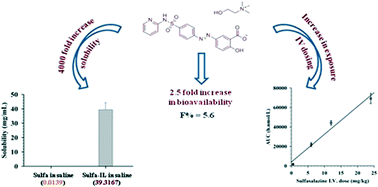
The absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of a cholinium ionic liquid (IL) salt of the poorly soluble drug sulfasalazine were evaluated in both in vitro and in vivo models. The IL exhibited about a 4000-fold improvement in saline solubility over the neutral drug and the improved solubility was translated to corresponding improvement in exposure where dose linear exposure after intravenous I.V. administration was demonstrated. Upon administration to rats, a sulfasalazine : choline chloride (1 : 1) physical mixture and the IL had equivalent I.V. exposures at a low solution dose of 0.5 mg kg−1. However, the superior solubility of the IL enabled administration of much higher I.V. doses (6, 12, and 24 mg kg−1, dissolved directly in saline), which resulted in a dose proportional increase in exposure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...