Intrinsically disordered amphiphilic peptides as potential targets in drug delivery vehicles
Abstract
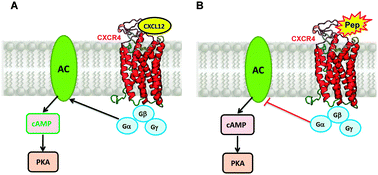
Intrinsically disordered proteins/peptides play a crucial role in many physiological and pathological events and may assume a precise conformation upon binding to a specific target. Recently, we have described the conformational and functional properties of two linear ester peptides provided with the following sequences: Y-G-E-C-P-C-K-OAllyl (PepK) and Y-G-E-C-P-C-E-OAllyl (PepE). Both peptides are characterized by the presence of the “CPC” motif together with a few amino acids able to promote disorder. The CPC sequence is a binding motif for the CXCR4 receptor that represents a well-known target for cancer therapies. In this paper, we report on synthetic amphiphilic peptides that consist of lipophilic derivatives of PepE and PepK bearing two stearic alkyl chains and/or an ethoxylic spacer. These peptide amphiphiles form stable supramolecular aggregates; they present conformational features that are typical of intrinsically disordered molecules as shown by CD spectroscopy. Solution fluorescence and DLS studies have been performed to evaluate Critical Micellar Concentrations and the dimension of supramolecular aggregates. Moreover, preliminary in vitro cell-based assays have been conducted to investigate the molecular recognition processes involving the CXCR4 receptor. In the end, the results obtained have been compared with the previous data generated by the corresponding non-amphiphilic peptides (PepE and PepK).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...