Collation and analyses of DNA-binding protein domain families from sequence and structural databanks†
Abstract
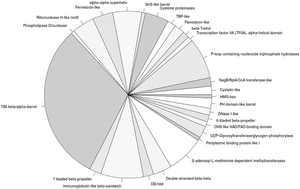
DNA–protein interactions govern several high fidelity cellular processes like DNA-replication, transcription, DNA repair, etc. Proteins that have the ability to recognise and bind DNA sequences can be classified either according to their DNA-binding motif or based on the sequence of the target nucleotides. We have collated the DNA-binding families by integrating information from both protein sequence family and structural databases. This resulted in a dataset of 1057 DNA-binding protein domain families. Their family properties (the number of members, percent identity distribution and length of members) and domain architectures were examined. Further, sequence domain families were mapped to structures in the protein databank (PDB) and the protein domain structure classification database (SCOP). The DNA-binding families, with no structural information, were clustered together into potential superfamilies based on sequence associations. On the basis of functions attributed to DNA-binding protein folds, we observe that a majority of the DNA-binding proteins follow divergent evolution. This study can serve as a basis for annotation and distribution of DNA-binding proteins in genome(s) of interest. The entire collated set of DNA-binding protein domains is available for download as Hidden Markov Models.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...