The potential of CAM crops as a globally significant bioenergy resource: moving from ‘fuel or food’ to ‘fuel and more food’†
Abstract
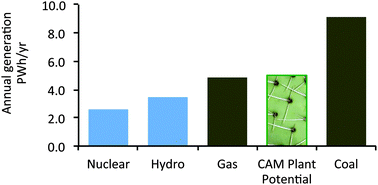
Bioenergy is widely seen as being in competition with food for land resources. This note examines the potential of plants that use the mode of photosynthesis known as crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) to generate globally significant quantities of renewable electricity without displacing productive agriculture and perhaps even increasing food supply. CAM plants require of the order of 10-fold less water per unit of dry biomass produced than do common C3 and C4 crops, and because of their succulence are endowed with substantial water-storage capacities that helps to buffer intermittent water availability. This allows them to thrive in areas where traditional agriculture struggles, either because of low rainfall, or because the seasonality or unpredictability of rainfall is too great to allow profitable arable farming. Although as a group these plants are understudied, sufficient data are available to support estimates of the contribution they might make to global electricity supply if used as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Two CAM species are examined here as potential bioenergy crops: Opuntia ficus-indica and Euphorbia tirucalli. Both show the high degree of drought tolerance typical of CAM plants and produce promising yields with low rainfall. Even CAM plants in semi-arid areas may have opportunity costs in terms of lost agricultural potential, but an alternative approach to bioenergy may allow the food value of land to be increased whilst using the land for energy. Global power generation from gas is around 5 PW h per year. The data suggests that 5 PW h of electricity per year could be generated from CAM plants cultivated on between 100 and 380 million hectares of semi-arid land, equivalent to between 4% and 15% of the potential resource.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...