Mechanism of proton transfer to coordinated thiolates: encapsulation of acid stabilizes precursor intermediate†
Abstract
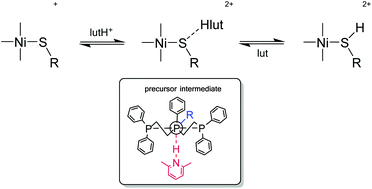
Earlier kinetic studies on the protonation of the coordinated thiolate in the square-planar [Ni(SC6H4R′-4)(triphos)]+ (R′ = NO2, Cl, H, Me or MeO) by lutH+ (lut = 2,6-dimethylpyridine) indicate a two-step mechanism involving initial formation of a (kinetically detectable) precursor intermediate, {[Ni(SC6H4R′-4)(triphos)]⋯Hlut}2+ (KR1), followed by an intramolecular proton transfer step (kR2). The analogous [Ni(SR)(triphos)]BPh4 {R = Et, But or Cy; triphos = PhP(CH2CH2PPh2)2} have been prepared and characterized by spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Similar to the aryl thiolate complexes, [Ni(SR)(triphos)]+ are protonated by lutH+ in an equilibrium reaction but the observed rate law is simpler. Analysis of the kinetic data for both [Ni(SR)(triphos)]+ and [Ni(SC6H4R′-4)(triphos)]+ shows that both react by the same mechanism, but that KR1 is largest when the thiolate is poorly basic, or the 4-R′ substituent in the aryl thiolates is electron-withdrawing. These results indicate that it is both NH⋯S hydrogen bonding and encapsulation of the bound lutH+ (by the phenyl groups on triphos) which stabilize the precursor intermediate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...