Reactivity of bis(organoamino)phosphanes with magnesium(ii) compounds†
Abstract
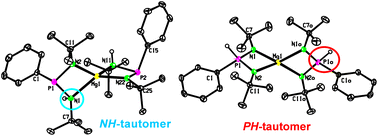
The reactivity of three phosphanes (PhP(NHR)2 [R = t-Bu (1), Ph (2)] and PhP(NEt2)(NHDip) (3) (where Dip = 2,6-i-Pr2C6H3)) with n-Bu2Mg and MeMgBr is presented. In the case of 1, the reaction with n-Bu2Mg gave [PhP(NHt-Bu)(Nt-Bu)]Mg(n-Bu) (4) or [PhP(NHt-Bu)(Nt-Bu)]2Mg (5) depending on the stoichiometry. The treatment of 1 with MeMgBr led to the phosphinate [Ph(H)P(Nt-Bu)2]2Mg (7) as a result of both the NH→PH tautomeric transformation and elimination of MgBr2 from the non-isolable intermediate [PhP(NHt-Bu)(Nt-Bu)]MgBr(THF) (6). Phosphane 2 reacted with n-Bu2Mg in a 1 : 1 molar ratio resulting in the formation of {[PhP(NPh)2]2Mg(THF)2}2 (8), but the analogous reaction in a 2 : 1 molar ratio yielded phosphinate [Ph(H)P(NPh)2]2Mg(THF) (9). The heteroleptic compound [Ph(H)P(NPh)2]MgBr(THF)2 (10) was obtained by the reaction of 2 with MeMgBr. Finally, the reaction of 3 with n-Bu2Mg and MeMgBr produced compounds [PhP(NEt2)(NDip)]2Mg (11) and {[PhP(NEt2)(NDip)2]Mg(μ-Br)(THF)}2 (12), respectively. All products were characterized using 1H, 13C{1H} and 31P NMR spectroscopy and, except for compounds 4 and 6, their molecular structures were determined using single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. In addition, a theoretical study on plausible isomers of 10 was performed to provide additional evidence for the presence of a syn- and anti-isomer in dynamic equilibrium in a solution of 10.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...