Structural and photoluminescence properties of stannate based displaced pyrochlore-type red phosphors: Ca3−xSn3Nb2O14:xEu3+†
Abstract
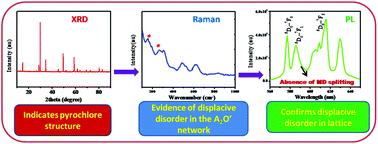
New stannate based displaced pyrochlore-type red phosphors, Ca3−xSn3Nb2O14:xEu3+, were prepared via a conventional solid state method. The influence of partial occupancy of Sn in both A and B sites of the pyrochlore-type oxides on the photoluminescence properties was studied using powder X-ray diffraction, FT-Raman, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive spectrometry, UV-visible absorption spectroscopy, and photoluminescence excitation and emission spectra with lifetime measurements. The structural analysis establishes that these oxides belong to a cubic displaced pyrochlore type structure with a space group Fd![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m. These phosphors exhibit strong absorptions at near UV and blue wavelength regions and emit intense multiband emissions due to Eu3+ 5D0–7F0, 1, 2 transitions. The absence of characteristic MD transition splitting points out that local cation disorder exists in this type of displaced pyrochlores, reducing the D3d inversion symmetry, which is not evidenced by such disorder in the X-ray diffraction analysis. The unusual forbidden intense sharp 5D0–7F0 transition indicates single site occupancy of Eu3+ with a narrower range of bonding environment, preventing the cluster formation. This is supported by the stable 5D0 lifetime with Eu3+ concentration. The Judd–Ofelt intensity parameter assessment corroborates these results. The CIE color coordinates of these phosphors were found to be (0.60, 0.40), which are close to the NTSC standard values (0.67, 0.33) for a potential red phosphor.
m. These phosphors exhibit strong absorptions at near UV and blue wavelength regions and emit intense multiband emissions due to Eu3+ 5D0–7F0, 1, 2 transitions. The absence of characteristic MD transition splitting points out that local cation disorder exists in this type of displaced pyrochlores, reducing the D3d inversion symmetry, which is not evidenced by such disorder in the X-ray diffraction analysis. The unusual forbidden intense sharp 5D0–7F0 transition indicates single site occupancy of Eu3+ with a narrower range of bonding environment, preventing the cluster formation. This is supported by the stable 5D0 lifetime with Eu3+ concentration. The Judd–Ofelt intensity parameter assessment corroborates these results. The CIE color coordinates of these phosphors were found to be (0.60, 0.40), which are close to the NTSC standard values (0.67, 0.33) for a potential red phosphor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...