Controlling the redox properties of a pyrroloquinolinequinone (PQQ) derivative in a ruthenium(ii) coordination sphere†
Abstract
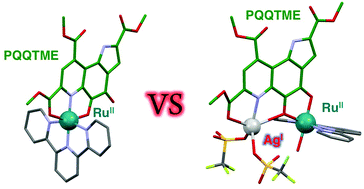
Ruthenium(II) complexes of PQQTME, a trimethyl ester derivative of redox-active PQQ (pyrroloquinolinequinone), were prepared using a tridentate ligand, 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine (terpy) as an auxiliary ligand. The characterization of the complexes was performed by spectroscopic methods, X-ray crystallography, and electrochemical measurements. In one complex, the pyridine site of PQQTME binds to the [RuII(terpy)] unit as a tridentate ligand, and a silver(I) ion is coordinated by the quinone moiety in a bidentate fashion. In contrast, another complex includes the [RuII(terpy)] unit at the bidentate quinone moiety of the PQQTME ligand. The difference in the coordination modes of the complexes exhibits a characteristic difference in the stability of metal coordination and also in the reversibility of the reduction processes of the PQQTME ligand. It should be noted that an additional metal-ion-binding to the PQQTME ligand largely raises the 1e−-reduction potential of the ligand. In addition, we succeeded in the characterization of the 1e−-reduced species of the complexes, where the unpaired electron was delocalized in the π-conjugated system of the PQQTME˙− ligand, using UV-Vis absorption and ESR spectroscopies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...