Graphene/nano-porous silicon and graphene/bimetallic silicon nanostructures (Pt–M, M: Pd, Ru, Rh), efficient electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction
Abstract
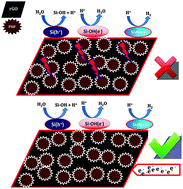
In this work nano-porous silicon flour (Nano-PSiF) was synthesized first and then there was an investigation into its electrocatalytic activity for the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The results showed that Nano-PSiF has good electrocatalytic activity for the HER when compared with PSiF. In the second section, Pt and Pt–M (M = Pd, Rh, Ru) bimetallic silicon nanostructures were prepared by a direct reduction of the metal (Pt, Pt–Pd, Pt–Rh and Pt–Ru) on the surface of the PSiF by a galvanic exchange mechanism. The electrocatalytic activity of the bimetallic silicon nanostructures (Pt–M/PSiF) were evaluated for the HER. The results showed that all of the Pt–M/PSiFs have excellent electrocatalytic activity for the HER in a 0.5 mol L−1 H2SO4 solution. For the Pt/PSiF, the Tafel slope of Pt/PSiF was 46.9 mV dec−1, indicating its excellent electrocatalytic activity for the HER and it is comparable with commercial Pt/C. On the other hand, the bimetallic silicon nanostructures showed better electrocatalytic activity than Pt/PSiF for the HER (lower Tafel slope, and higher α). Finally, exfoliated graphene oxide was electro-deposited on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode (eRGO/GCE) and used as a sub-layer for the Pt–M/PSiF. Then, the electrocatalytic activities of the bimetallic silicon nanostructures on the eRGO/GCE were investigated for the HER. The results showed that there was a higher electrocatalytic activity for Pt–M/PSiF–eRGO/GCE when compared with Pt–M/PSiF–GCE.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...