High-resolution probing heparan sulfate–antithrombin interaction on a single endothelial cell surface: single-molecule AFM studies†
Abstract
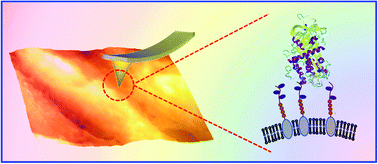
Heparan sulfate (HS) plays diverse functions in multiple biological processes by interacting with a wide range of important protein ligands, such as the key anticoagulant factor, antithrombin (AT). The specific interaction of HS with a protein ligand is determined mainly by the sulfation patterns on the HS chain. Here, we reported the probing single-molecule interaction of AT and HS (both wild type and mutated) expressed on the endothelial cell surface under near-physiological conditions by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Functional AFM imaging revealed the uneven distribution of HS on the endothelial cell surface though they are highly expressed. Force spectroscopy measurements using an AT-functionalized AFM tip revealed that AT interacts with endothelial HS on the cell surface through multiple binding sites. The interaction essentially requires HS to be N-, 2-O- and/or 6-O-sulfated. This work provides a new tool to probe the HS-protein ligand interaction at a single-molecular level on the cell surface to elucidate the functional roles of HS.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...