A crossed molecular beam and ab initio study on the formation of 5- and 6-methyl-1,4-dihydronaphthalene (C11H12) via the reaction of meta-tolyl (C7H7) with 1,3-butadiene (C4H6)†
Abstract
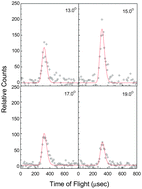
The crossed molecular beam reactions of the meta-tolyl radical with 1,3-butadiene and D6-1,3-butadiene were conducted at collision energies of 48.5 kJ mol−1 and 51.7 kJ mol−1. The reaction dynamics propose a complex-forming reaction mechanism via addition of the meta-tolyl radical with its radical center either to the C1 or C2 carbon atom of the 1,3-butadiene reactant forming two distinct intermediates, which are connected via migration of the meta-tolyl group. Considering addition to C1 proceeds by formation of a van-der-Waals complex below the energy of the separated reactants, we propose that in cold molecular clouds holding temperatures as low as 10 K, the reaction of the meta-tolyl radical with 1,3-butadiene is de-facto barrier less. At elevated temperatures such as in combustion processes, the reaction can also proceed via addition to C2 by overcoming the entrance barrier to addition (11 kJ mol−1). Eventually, the resonantly stabilized free radical intermediate C11H13 undergoes isomerization to a cis form, followed by rearrangement through two distinct ring closures at the para- and ortho-position of tolyl radical to yield cyclic intermediates. These intermediates then emit a hydrogen atom forming 6- and 5-methyl-1,4-dihydronaphthalene via tight exit transition states. The steady state branching ratio, 70.0% and 29.2%, at the collision energy of 51.7 kJ mol−1, of 6- and 5-methyl-1,4-dihydronaphthalene, respectively, is determined mainly by the rates of reverse ring opening of cyclic intermediates. The formation of the thermodynamically less stable 1-meta-tolyl-trans-1,3-butadiene was found to be a less important pathway (0.8%). The reaction of the meta-tolyl radical with 1,3-butadiene leads without entrance barrier to two methyl substituted PAH derivatives holding 1,4-dihydronapthalene cores: 5- and 6-methyl-1,4-dihydronaphthalene thus providing a barrierless route to odd-numbered PAH derivatives under single collision conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...